- 1. 小数转换为百分数
- 2. 文件操作
- 3. 读写csv文件
- 4. python3.6读ini配置文件
- 5. django之允许外部机器访问本机服务
- 6. Python多进程并发操作中进程池Pool的应用
- 7. 进程池使用queue队列
- 8. operator.itemgetter()
- 9. sorted()内建函数
- 10. python2.7 解决UnicodeDecodeError: ‘ascii’ codec can’t decode byte 0xe5 in position 108: ordinal not in range(128。。。。
- 11. 几个有用的python函数 (笛卡尔积, 排列, 组合)
- 12. python求两个链表组成的数字的和
- 13. python内置函数——divmod(a, b)
- 14. python内置函数——enumerate(sequence, start=0)
- 15. python内置函数——filter(function, iterable)
- 16. datetime
- 17. 针对“could not install packages due to an EnvironmentError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: ‘/Library/Python/2.7/site-packages/vine’”的解决方式
- 18. 字典转xml
- 19. or和and
- 20. xmltodict的坑
- 21. 列表生成式中的if-else
- 22. 针对MySQL said: Authentication plugin ‘caching_sha2_password’ cannot be loaded: dlopen(/usr/local/…的问题
- 23. django model获取特定字段
- 24. Connection reset by peer的常见原因
1. 小数转换为百分数
1 | def change_percent(num): |
2. 文件操作
查看当前目录
1
os.getcwd()
或
1
2
3
4from os import path
d = path.dirname(__file__)
# __file__ 为当前文件, 若果在ide中运行此行会报错,可改为 #d = path.dirname('.')获得单个目录节点的子节点
1
os.listdir(rootdir)
获取当前目录下的信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10for parent,dirnames,filenames in os.walk(rootdir): #三个参数:分别返回1.父目录 2.所有文件夹名字(不含路径)3.所有文件名字
for dirname in dirnames: #输出文件夹信息
print "parent is:" + parent
print "dirname is" + dirname
for filename in filenames: #输出文件信息
print "parent is:" + parent
print "filename is:" + filename
print "the full name of the file is:" + os.path.join(parent,filename) #输出文件路径信息
3. 读写csv文件
写入
1
2
3
4
5
6import csv
def writer_to_csv(info):
result_csv = open('result.csv', 'a', encoding='utf8')
writer = csv.writer(result_csv)
writer.writerow(info)
result_csv.close()读出
1
2
3
4
5
6import csv
def read_csv(file):
csv_file = open(file, 'r')
reader = csv.reader(csv_file)
for item in reader:
yield item[0]
4. python3.6读ini配置文件
说明:python2.7-3.5使用的是ConfigParser模块
1 | import configparser |
5. django之允许外部机器访问本机服务
开启django服务时,使用0.0.0.0:端口启动,例:
1
./manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:9999
修改setting文件中的ALLOWED_HOSTS
1
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*', ]
注意:
['*', ]一定要加,
6. Python多进程并发操作中进程池Pool的应用
说明:
- 使用
Pool类,需要通过from multiprocessing import Pool导入池 - join方法必须在close或terminate之后使用。
- 使用
apply_async()
函数原型:
apply_async(func[, args=()[, kwds={}[,callback=None]]]),该方法非阻塞且支持结果返回进行回调。示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31import time
from multiprocessing import Pool
def run(fn):
# fn: 函数参数是数据列表的一个元素
time.sleep(1)
return fn * fn
if __name__ == "__main__":
testFL = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
print('顺序执行:') # 顺序执行(也就是串行执行,单进程)
s = time.time()
for fn in testFL:
print(run(fn))
e1 = time.time()
print("顺序执行时间:", int(e1 - s))
print('多进程执行:') # 创建多个进程,并行执行
pool = Pool(5) # 创建拥有5个进程数量的进程池
# testFL:要处理的数据列表,run:处理testFL列表中数据的函数
# rl = pool.map(run, testFL)
for fn in testFL:
pool.apply_async(run, args=(fn, ))
pool.close() # 关闭进程池,不再接受新的进程
pool.join() # 主进程阻塞等待子进程的退出
e2 = time.time()
print("并行执行时间:", int(e2 - e1))
# print(rl)响应:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10顺序执行:
1
4
9
16
25
36
顺序执行时间: 6
多进程执行:
并行执行时间: 2
map()
函数原型:
map(func, iterable[, chunksize=None]),Pool类中的map方法,与内置的map函数用法行为基本一致,它会使进程阻塞直到返回结果。
注意:虽然第二个参数是一个迭代器,但在实际使用中,必须在整个队列都就绪后,程序才会运行子进程。示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31import time
from multiprocessing import Pool
def run(fn):
# fn: 函数参数是数据列表的一个元素
time.sleep(1)
return fn * fn
if __name__ == "__main__":
testFL = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
print('顺序执行:') # 顺序执行(也就是串行执行,单进程)
s = time.time()
for fn in testFL:
print(run(fn))
e1 = time.time()
print("顺序执行时间:", int(e1 - s))
print('多进程执行:') # 创建多个进程,并行执行
pool = Pool(5) # 创建拥有5个进程数量的进程池
# testFL:要处理的数据列表,run:处理testFL列表中数据的函数
rl = pool.map(run, testFL)
# for fn in testFL:
# pool.apply_async(run, args=(fn, ))
pool.close() # 关闭进程池,不再接受新的进程
pool.join() # 主进程阻塞等待子进程的退出
e2 = time.time()
print(rl)
print("并行执行时间:", int(e2 - e1))响应:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11顺序执行:
1
4
9
16
25
36
顺序执行时间: 6
多进程执行:
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36]
并行执行时间: 2
7. 进程池使用queue队列
注意:进程池使用队列,应使用Manager对象的Queue
1 | from multiprocessing import Manager |
8. operator.itemgetter()
返回一个可调用对象,该对象使用被操作元的**__getitem__()方法从其被操作元获取项**。通过该函数作用到对象上才能获取值。如果指定了多个项,则返回查找值的一组。例如:
- 在f = itemgetter(2)之后,调用f(r)返回r[2]。
- 在g = itemgetter(2,5,3)之后,调用g(r)返回(r[2], r[5], r[3])。
等价于:
1 | def itemgetter(*items): |
项可以是被操作元的**__getitem__()**方法所接受的任何类型。字典接受各种哈希值,列表、元组和字符串接受索引或片:
1 | >>> itemgetter(1)('ABCDEFG') |
在版本2.5中更改:添加了对多个项目提取的支持。
使用itemgetter()从元组记录中检索特定字段的示例:
1 | >>> inventory = [('apple', 3), ('banana', 2), ('pear', 5), ('orange', 1)] |
9. sorted()内建函数
sort 与 sorted 区别:
- sort 是应用在 list 上的方法,sorted 可以对所有可迭代的对象进行排序操作。
- list 的 sort 方法返回的是对已经存在的列表进行操作,而内建函数 sorted 方法返回的是一个新的 list,而不是在原来的基础上进行的操作。
sorted 语法:
sorted(iterable[, cmp[, key[, reverse]]])
参数说明:
- iterable – 可迭代对象。
- cmp – 比较的函数,这个具有两个参数,参数的值都是从可迭代对象中取出,此函数必须遵守的规则为,大于则返回1,小于则返回-1,等于则返回0。
- key – 主要是用来进行比较的元素,只有一个参数,具体的函数的参数就是取自于可迭代对象中,指定可迭代对象中的一个元素来进行排序。
- reverse – 排序规则,reverse = True 降序 , reverse = False 升序(默认)。
例子:
1 | >>>a = [5,7,6,3,4,1,2] |
注意:建议使用key,而不是cmp,因为key更节省内存空间
10. python2.7 解决UnicodeDecodeError: ‘ascii’ codec can’t decode byte 0xe5 in position 108: ordinal not in range(128。。。。
出现错误原因:
python的str默认是ascii编码,和unicode编码冲突
解决方案:
import sys
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding(‘utf8’)
11. 几个有用的python函数 (笛卡尔积, 排列, 组合)
- product 笛卡尔积
- permutations 排列
- combinations 组合,没有重复
- combinations_with_replacement 组合,有重复
1 | >>> import itertools |
12. python求两个链表组成的数字的和
给定两个非空链表来表示两个非负整数。位数按照逆序方式存储,它们的每个节点只存储单个数字。将两数相加返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头
示例:
输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 0 -> 8
原因:342 + 465 = 807
代码实现:
1 | # Definition for singly-linked list. |
13. python内置函数——divmod(a, b)
v2.7
实际上是算a除以b的商和余数,返回(商,余数)
1
2
3
4divmod(1,2)
(0, 1)
divmod(5, 1)
(5, 0)
14. python内置函数——enumerate(sequence, start=0)
1 | >>> seasons = ['Spring', 'Summer', 'Fall', 'Winter'] |
15. python内置函数——filter(function, iterable)
v2.7
如果function是None,就等价于:
[item for item in iterable if item]
如果function不是None,就等价于:
[item for item in iterable if function(item)]
16. datetime
datetime模块用于是date和time模块的合集,datetime有两个常量,MAXYEAR和MINYEAR,分别是9999和1.
datetime模块定义了5个类,分别是
1. datetime.date:表示日期的类
2. datetime.datetime:表示日期时间的类
3. datetime.time:表示时间的类
4. datetime.timedelta:表示时间间隔,即两个时间点的间隔
5. datetime.tzinfo:时区的相关信息
datetime.date类
date类有三个参数,datetime.date(year,month,day),返回datetime.date(2018, 7, 30)datetime.date.ctime(),返回格式如 Sun Apr 16 00:00:00 2017
1
2>>>datetime.date.ctime(datetime.date(2018, 7, 30))
'Mon Jul 30 00:00:00 2018'datetime.date.fromtimestamp(timestamp),根据给定的时间戮,返回一个date对象;**datetime.date.today()**作用相同
1
2>>>datetime.date.today()
datetime.date(2018, 7, 30)datetime.date.isocalendar():返回格式如(year,month,day)的元组
1
2>>>datetime.date.isocalendar(datetime.date(2018, 7, 30))
(2018, 31, 1)**datetime.date.isoformat()**:返回格式如YYYY-MM-DD
1
2>>>datetime.date.isoformat(datetime.date(2018, 7, 30))
'2018-07-30'**datetime.date.isoweekday()**:返回给定日期的星期(0-6),星期一=0,星期日=6
1
2>>>datetime.date.isoweekday(datetime.date.today())
1**datetime.date.replace(year,month,day)**:替换给定日期,但不改变原日期
1
2
3>>>a = datetime.date.today()
>>>a.replace(day=26)
datetime.date(2018, 7, 26)datetime.date.strftime(format):把日期时间按照给定的format进行格式化。
1
2>>>datetime.date.strftime(datetime.date.today(), '%Y-%m-%d')
'2018-07-30'1
2
3
4
5>>>a = datetime.date.today()
>>>a
datetime.date(2018, 7, 30)
>>>a.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
'2018-07-30'**datetime.date.timetuple()**:返回日期对应的time.struct_time对象
1
2
3>>>a = datetime.date.today()
>>>datetime.date.timetuple(a)
time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=30, tm_hour=0, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=211, tm_isdst=-1)**datetime.date.weekday()**:返回日期的星期
1
2
3
4
5
6>>>a = datetime.date.today()
>>>datetime.date.weekday(a)
0
>>>a.weekday()
0
datetime.time类
time类有5个参数,datetime.time(hour,minute,second,microsecond,tzoninfo),返回08:29:30datetime.time.replace()
1
2>>>datetime.time.replace(datetime.time(), hour=1)
datetime.time(1, 0)datetime.time.strftime(format):按照format格式返回时间
1
2>>>datetime.time.strftime(datetime.time(2,3), "%H:%M")
'02:03'**datetime.time.tzname()**:返回时区名字
**datetime.time.utcoffset()**:返回时区的时间偏移量
datetime.datetime类
datetime类有很多参数,datetime(year, month, day[, hour[, minute[, second[,microsecond[,tzinfo]]]]]),返回年月日,时分秒datetime.datetime.ctime()
**datetime.datetime.now().date()**:返回当前日期时间的日期部分
**datetime.datetime.now().time()**:返回当前日期时间的时间部分
datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp()
**datetime.datetime.now()**:返回当前系统时间
datetime.datetime.replace()
**datetime.datetime.strftime()**:由日期格式转化为字符串格式
1
2>>>datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%b-%d-%Y %H:%M:%S')
'Apr-16-2017 21:01:35'datetime.datetime.strptime():由字符串格式转化为日期格式
1
2>>>datetime.datetime.strptime('Apr-16-2017 21:01:35', '%b-%d-%Y %H:%M:%S')
2017-04-16 21:01:35
datetime.timedelta类
datetime.datetime.timedelta用于计算两个日期之间的差值,例如:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11>>> a=datetime.datetime.now()
>>> b=datetime.datetime.now()
>>> a
datetime.datetime(2017, 4, 16, 21, 21, 20, 871000)
>>> b
datetime.datetime(2017, 4, 16, 21, 21, 29, 603000)
>>> b-a
datetime.timedelta(0, 8, 732000)
>>> (b-a).seconds
8或者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7time1 = datetime.datetime(2016, 10, 20)
time2 = datetime.datetime(2015, 11, 2)
"""计算天数差值"""
print(time1-time2).days
"""计算两个日期之间相隔的秒数"""
print (time1-time2).total_seconds()
17. 针对“could not install packages due to an EnvironmentError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: ‘/Library/Python/2.7/site-packages/vine’”的解决方式
1 | pip install --user flask |
在install后加–user
18. 字典转xml
v2.7
dicttoxml会自动在头部添加<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
并通过参数设置xml的属性1
2import dicttoxml
dicttoxml.dicttoxml(self.post_data_dict, root=True, custom_root="request", attr_type=False)
19. or和and
如果用or,应该把为true的写在or前,减小运算时间;
如果用and,应该把false的写在and前
20. xmltodict的坑
- 如果xml中在同一级有相同元素,就会把相同元素变成列表;如果没有相同元素,那么就把该元素变为字典
- 对于xml中为空的情况,xmltodict会自动将值变为
None
21. 列表生成式中的if-else
只有if
1
[a for a in a_list if a==1]
if-else
1
[a if a==1 else a-1 for a in a_list]
22. 针对MySQL said: Authentication plugin ‘caching_sha2_password’ cannot be loaded: dlopen(/usr/local/…的问题
在使用MySQL Workbench连接本地数据库的时候,出现了
1 | MySQL said: Authentication plugin 'caching_sha2_password' cannot be loaded: dlopen(/usr/local/lib/plugin/caching_sha2_password.so, 2): image not found |
这是因为在链接数据库时不能加载‘caching_sha2_password’这个插件,也就是不能对身份验证。
解决方案是:
1. 打开系统偏好设置,找到mysql,点击Initialize Database。
2. 输入你的新密码,记住这个密码,用于后期链接数据库的登陆使用。
3. 选择‘Use legacy password‘。
4. 重启mysql服务。
这样在连接就没有问题了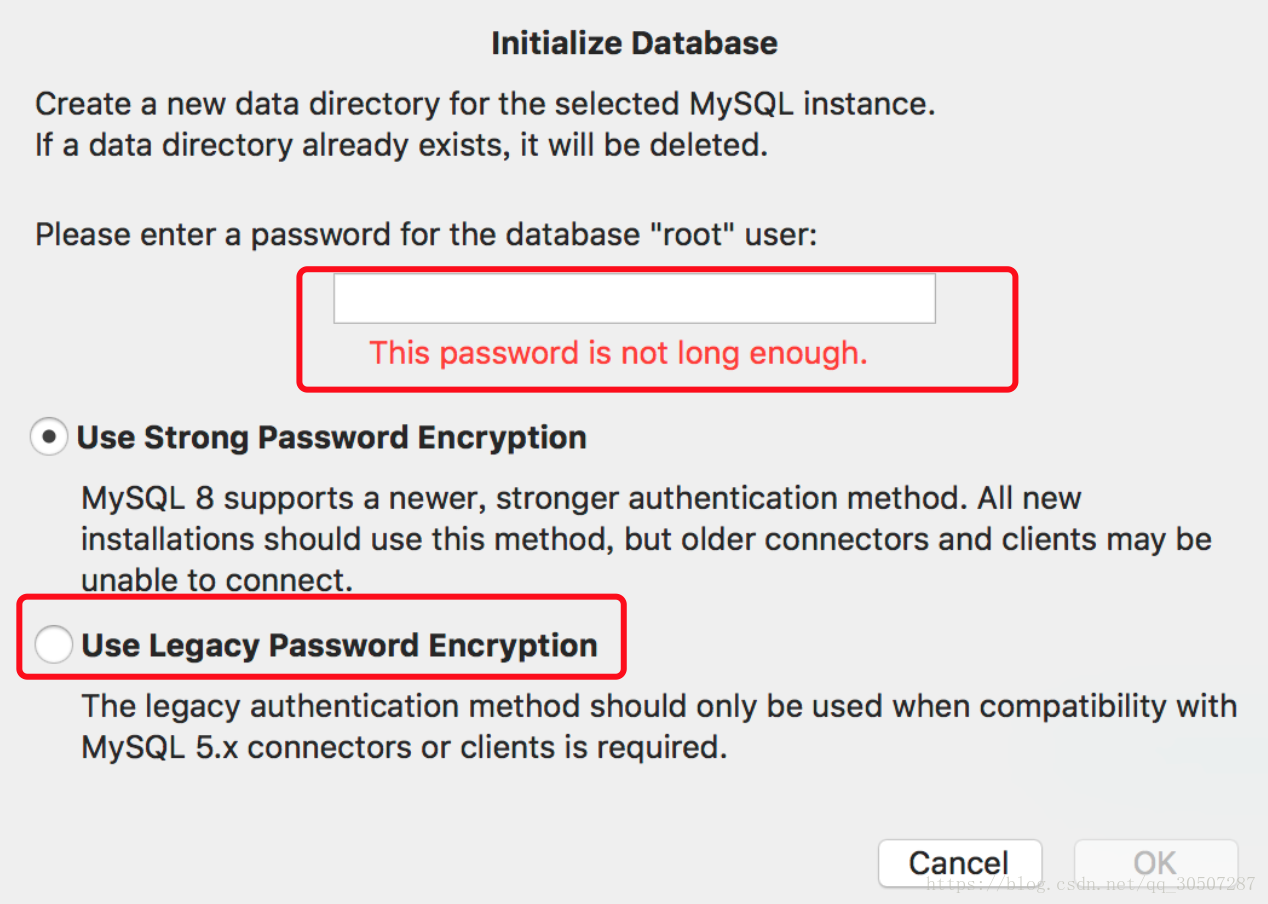
23. django model获取特定字段
1 | comment_list = Comment.objects.all()[:5].only('post', 'text') # 只获取特定字段 |
24. Connection reset by peer的常见原因
Connection reset by peer: socket write error错误分析:
常出现的Connection reset by peer: 原因可能是多方面的,不过更常见的原因是:
①:服务器的并发连接数超过了其承载量,服务器会将其中一些连接Down掉;
②:客户关掉了浏览器,而服务器还在给客户端发送数据;
③:浏览器端按了Stop
通常原因为:远程主机上对等方应用程序突然停止运行,或远程主机重新启动,或远程主机在远程方套接字上使用了“强制”关闭 (参见setsockopt(SO_LINGER))。另外,在一个或多个操作正在进行时,如果连接因“keep-alive”活动检测到一个失败而中 断,也可能导致此错误。此时,正在进行的操作以错误码WSAENETRESET失败返回,后续操作将失败返回错误码WSAECONNRESET。
但是如果频繁出现,就表示很 多客户端连接到Apache服务器的响应时间太长了,可能是网络的问题或者服务器性能问题。